

1.8.5 describe the trend in oxidising ability of the halogens down the Group applied to displacement reactions of the halogens with other halide ions in solution.1.8.4 recall the reaction of chlorine with water to form chloride ions and chlorate(I) ions.1.8.2 compare the solubility and colours of the halogens in water and non-aqueous solvents, for example hexane.Unit AS 1: Basic Concepts in Physical and Inorganic Chemistry.1.9.15 describe the tests for the following: chloride, bromide and iodide (using silver nitrate solution).1.6.19 investigate the displacement reactions of Group 7 (VII) elements with solutions of other halides to establish the trend in reactivity within the group and make predictions based on this trend.Unit 1: Structures, Trends, Chemical Reactions, Quantitative Chemistry and Analysis.C4.2b describe tests to identify aqueous cations and aqueous anions.C4.2 Identifying the products of chemical reactions.C4 Predicting and identifying reactions and products.C5.2.4 describe tests to identify aqueous cations and aqueous anions and identify species from test results including: tests and expected results for metal ions in solution by precipitation reactions using dilute sodium hydroxide (calcium, copper, iron(I….C5.2 How do chemists find the composition of unknown samples?.C2.2.6 recall the simple properties of Group 7 elements including their states and colours at room temperature and pressure, their colours as gases, their reactions with Group 1 elements and their displacement reactions with other metal halides.

C2.2 What does the Periodic Table tell us about the elements?.6.11 Describe the relative reactivity of the halogens chlorine, bromine and iodine, as shown by their displacement reactions with halide ions in aqueous solution, and use this pattern to predict the reactions of astatine.6.10 Recall that the halogens, chlorine, bromine and iodine, form hydrogen halides which dissolve in water to form acidic solutions, and use this pattern to predict the reactions of other halogens.9.5Cc chloride ion, Cl⁻, bromide ion, Br⁻, iodide ion, I⁻, using dilute nitric acid and silver nitrate solution.

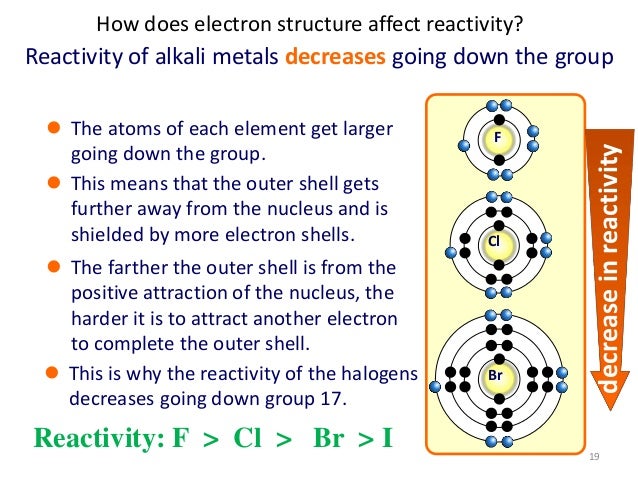
The silver nitrate solution is acidified.Students should be able to explain why: silver nitrate solution is used to identify halide ions.The trend in solubility of the silver halides in ammonia.The use of acidified silver nitrate solution to identify and distinguish between halide ions.The trend in reducing ability of the halide ions, including the reactions of solid sodium halides with concentrated sulfuric acid.The trend in oxidising ability of the halogens down the group, including displacement reactions of halide ions in aqueous solution.RSC Yusuf Hamied Inspirational Science Programme.Introductory maths for higher education.The physics of restoration and conservation.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
